Water Cement Ratio – Definition, Calculation, Complete Guide.
What is Water Cement Ratio?
The ratio between the water and cement by weight is known as Water-Cement Ratio.
The quantity of water added to the cement while preparing concrete mixes has been known to exert tremendous influence on the quality of concrete.
It was first discovered in 1918 A.D. Abraham had evaluated this aspect of concrete proportioning and stated:
Abraham stated that: The strength of Concrete / Mortaris dependent on the net quantity of water used per sack of cement.
Water can also affect the whole properties, the durability, strength of concrete to a great extent.
Therefore, you need to use the amount of water very carefully in the mix.
Too much water can increase the workability, but it will also adversely effect the strength and durability of concrete.
And water used in a small amount can increase the strength and durability of concrete but will decrease its workability.
That’s why you need to carefully select the quantity of water which should be used in the mix.
Functions of Water in Concrete.
As said, earlier water performs two essential functions in concrete:
- It hydrates the cement, which is an essential chemical reaction for formation of complex silicate crystalline gels that are responsible for the strength of the cement.
- It lubricates all the concrete ingredients, by passing around them in the form of films. Hence it is responsible for the plasticity and mobility of concrete which define its workability.
Workability of Concrete: The ease with which the concrete can be transported, placed without any segregation is known as workability of concrete.
Workability of concrete depends upon the quantity of water used in it.
How to calculate Water Cement Ratio?
In order to determine the water-cement ratio for the particular type of aggregates, trial mixes are made keeping in view the water-cement-strength ratios.
A lot of data is available on the latter relationship in all works on concrete construction. One such relationship is produced below in table as an illustrg class=”size-full wp-image-332 aligncenter” src=”https://civilseek.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Water-Cement-Ratio-Table.jpg” alt=”Water-Cement-Ratio-Table” width=”707″ height=”279″ />
The above effect of the decrease in compressive strength with an increase in water-cement ratio is also illustrated graphically.
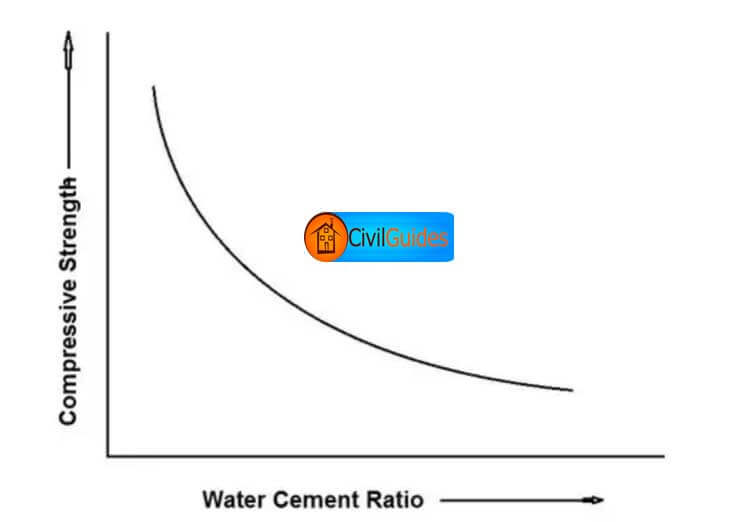
For a given type of cement, aggregates of same type and size, and same methods of mixing, the concrete develops a maximum compressive strength of 380 Kg/cm2 at a W/C=0.4.
When this ratio is increased to 0.5, 0.6 and 0.7, etc., The resulting batches of concrete show considerably less compressive strength.
It has been established from theoretical studies and experimental investigations that for ordinary Portland Cement, ” 1 part of cement (by weight) will require about 0.25 parts of water (by weight) for complete hydration, setting, and hardening of concrete/mortar.”
Naturally, while preparing a concrete mix, this much water is sufficient only for hydration. For lubrication and workability of the mix, additional water must be added.
This additional quantity if water varies from 0.15 to 0.45 parts by weight and has to be determined with great caution.
The most important aspect of this additional (lubricating) water is that it evaporates after the concrete is placed. Water is also released during compaction.
Effect of Excessive Water on Concrete-Mix
Both of the above processes (of the escape of additional water) result in voids in the concrete. And the development of voids always reduces its strength.
Hence, an attempt is made to keep the “Water Cement Ratio” as low as possible to obtain a strong, dense concrete-mix.
Any extra amount of water added to concrete ingredients at the time of mixing also cause segregation of aggregates during transport and placement.
This is another defect of extra water added to concrete-mix.
Water Quantity Calculation for Concrete.
For the calculation of water quantity for concrete, first of all, we have to find the quantity of cement.
Just assume that the required volume of cement for the mix is 100 kg and W/C is 0.4.
Water Quantity = Water-Cement Ratio x Volume of Cement.
Water Quantity = 0.4 x 100 kg = 40 liters / 100 kg cement or (20 liters / 50 kg cement bag).
Watch the Video Below for better understanding.
Test to Calculate Water-Cement Ratio.
Now, as you have calculated the water-cement ratio and quantity of water from the above steps. So, now you need to test that calculated W/C practically.




